Contract interactions
The Contract interactions project is designed to demonstrate how you can import and use functions defined in one module in another module. For this project, you'll build a smart contract with separate modules to handle user authorization and payments with secure interactions between the modules. Secure contract interaction is a fundamental requirement for setting up more complex smart contracts.
For this project, you'll create two Pact modules:
- An
authmodule for authorizing operations based on theidstored for the user in a table. - A
paymentsmodule for managing account balances and transferring value between accounts.
The following diagram provides an overview of the interaction between the modules.
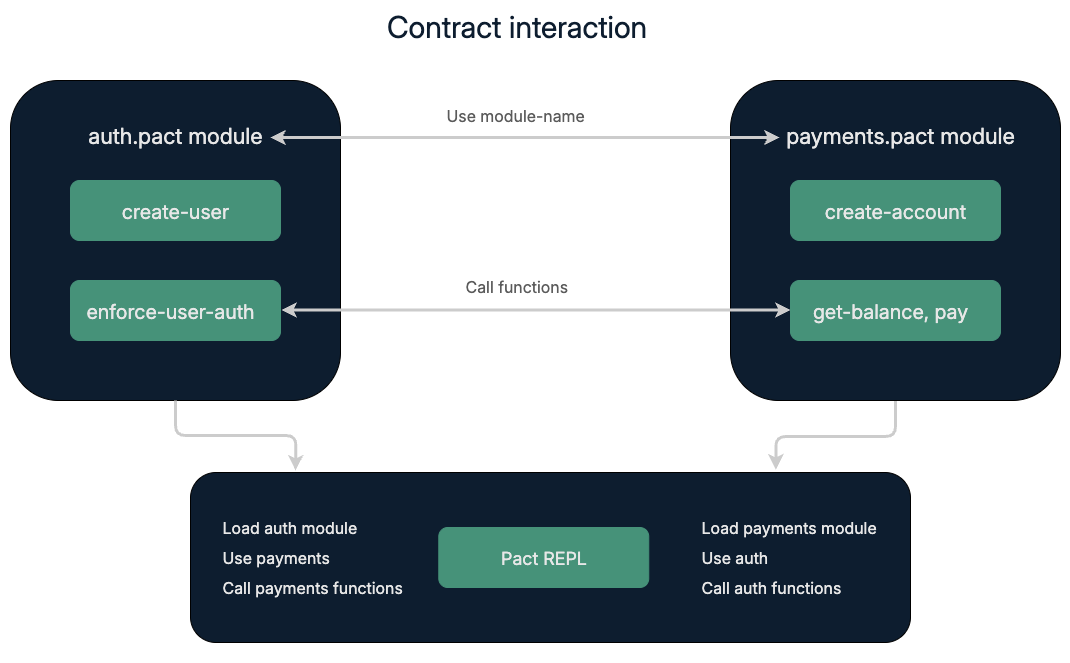
To demonstrate contract interoperation, you'll also create test accounts for an administrator and two users, Sarah and James.
In this tutorial, you'll learn about the following topics:
- Calling contract functions defined in one module for use in another module.
- Setting up separate modules for authorization and payments.
- Testing contract interactions in the REPL environment.
Before you begin
Before starting this project, verify your environment meets the following basic requirements:
- You have a GitHub account and can run
gitcommands. - You have installed the Pact programming language and command-line interpreter.
- You have installed the
kadena-clipackage and have a working directory with initial configuration settings. - You have a local development node that you can connect to that runs the
chainweb-nodeprogram, either in a Docker container or on a physical or virtual computer. - You must have at least one account that's funded with KDA on at least one chain for deployment on the local development network or the Kadena test network.
- You should be familiar with the basics for defining modules and using keysets.
Get the starter code
To get started:
-
Open a terminal shell on your computer.
-
Clone the
pact-coding-projectsrepository by running the following command:git clone https://github.com/kadena-docs/pact-coding-projects.git -
Change to the
03-contract-interactionsdirectory by running the following command:cd pact-coding-projects/03-contract-interactionsIf you list the contents of this directory, you'll see that there are folders for
starter-contractsandfinished-contracts. Thestarter-contractsfolder includes the following files:auth.pactprovides the basic framework for coding theauthmodule.payments.pactprovides the basic framework for coding thepaymentsmodule.starter-contract-interaction.pactprovides a framework overview of the complete coding project.contract-interaction.replprovides the basic framework for building a.replfile with test cases for verifying module interactions.
-
Open and review the
starter-contract-interaction.pactfile for an overview of the tasks you need to complete for the Contract Interactions project. Yo can follow the embedded instructions to work through the coding challenges on your own or use the detailed instructions provided in the next sections.
Key concepts for contract interaction
In Pact, modules can call functions from other modules, enabling more complex contract setups. You’ll be using the following key Pact features:
- load to load and evaluate a module.
- use to import an existing module into a namespace.
- function calls to invoke functions in the one module that are defined in another module.
Getting started
You’ll work with three main files:
- auth.pact - Responsible for authorizing users.
- payments.pact - Manages payments between users.
- payments.repl - Coordinates interactions between the modules.
Define the auth module
As you might have seen in other coding projects, modules are defined in a namespace and are governed by either an administrative keyset or a governance capability.
To simplify the initial code required, this coding project assumes you are defining a custom dev namespace for local development.
As an alternative, you could use the free namespace.
The free namespace is a publicly-available namespace that you can use to deploy smart contracts on the Kadena test network.
The best practice is to create a unique principal namespace where you can deploy all of your modules.
If you have a principal namespace, use that namespace string instead of using the dev namespace.
To define the auth module:
-
Create an
auth.pactfile, then define and enter a custom, principal, or existing namespace.For example, add the following code to define a new
devnamespace and make it your active namespace:(define-namespace "dev" (read-keyset "module-admin-keyset") (read-keyset "module-admin-keyset"))
(namespace "dev") -
Define two keysets in the
auth.pactfile to identify the keysets that have access to module operations.(define-keyset "dev.module-admin" (read-keyset "module-admin-keyset"))
(define-keyset "dev.operate-admin" (read-keyset "module-operate-keyset"))These keysets will help manage access control throughout the contract.
-
Create the
authmodule with a governance capability that enforces themodule-adminkeyset guard.(module auth AUTH
(defcap AUTH ()
(enforce-guard "dev.module-admin")) -
Define the schema and table for managing user data.
(defschema user
nickname:string
keyset:guard)
(deftable users:{user}) -
Define the
create-userfunction thatoperate-adminkeyset owners can execute to add new users to theauthmodule.(defun create-user:string (id:string nickname:string keyset:guard)
(enforce-guard "dev.operate-admin")
(insert users id {
"keyset": keyset,
"nickname": nickname
})
) -
Define the
enforce-user-authfunction that ensures a user is authorized for a specific operation.(defun enforce-user-auth:guard (id:string)
(with-read users id { "keyset":= k }
(enforce-guard k)
k)
) -
Complete the
authmodule by closing the module declaration and create theuserstable.)
(create-table users)
Define the payments module
-
Create a
payments.pactfile, then define and enter the same custom, principal, or existing namespace you're using for theauthmodule. -
Define a keyset in the
payments.pactfile that will manage this module.(define-keyset "dev.module-admin" (read-keyset "module-admin-keyset")) -
Start the
paymentsmodule declaration and import theauthmodule with the Pactusekeyword.(module payments ADMIN
(defcap ADMIN ()
(enforce-guard "dev.module-admin"))
(use auth)
) -
Define the schema and table for account management.
(defschema account
balance:decimal)
(deftable accounts:{account}) -
Define the
create-accountfunction to set up a new account, ensuring the user is authorized.(defun create-account:string (userId:string initial-balance:decimal)
"Create a new account for ID with INITIAL-BALANCE funds, must be administrator."
(enforce-user-auth userId)
(enforce (>= initial-balance 0.0) "Initial balances must be >= 0.")
(insert accounts userId
{ "balance": initial-balance})
) -
Define the
get-balancefunction to retrieve the balance for an account from the database for an authorized user.(defun get-balance:decimal (userId:string)
"Only admin can read balance."
(enforce-user-auth "admin")
(with-read accounts userId
{ "balance":= balance }
balance)
) -
Define the
payfunction to allow for transferring funds between accounts.(defun pay:string (from:string to:string amount:decimal)
(with-read accounts from { "balance":= from-bal }
(enforce-user-auth from)
(with-read accounts to { "balance":= to-bal }
(enforce (> amount 0.0) "Transaction amount cannot be negative.")
(enforce (>= from-bal amount) "Insufficient funds")
(update accounts from
{ "balance": (- from-bal amount) })
(update accounts to
{ "balance": (+ to-bal amount) })
(format "{} paid {} {}" [from to amount])))
) -
Complete the
paymentsmodule by closing the module declaration and create theaccountstable.)
(create-table accounts)
Test interactions with the REPL File
To test contract interaction:
-
Create a
payments.replfile and add a transaction that loads theauth.pactmodule.(begin-tx)
(load "auth.pact")
(commit-tx) -
Add a transaction that loads the
payments.pactmodule.(begin-tx)
(load "payments.pact")
(commit-tx) -
Add a transaction that uses the
authmodule to create user accounts.(begin-tx)
(use auth)
(env-data {
"admin-keyset" : ["admin"],
"sarah-keyset": ["sarah"],
"james-keyset": ["james"]})
(create-user "admin" "Administrator" (read-keyset "admin-keyset"))
(create-user "sarah" "Sarah" (read-keyset "sarah-keyset"))
(create-user "james" "James" (read-keyset "james-keyset"))
(commit-tx) -
Add a transaction that uses the
paymentsmodule to test transactions.(begin-tx)
(use payments)
(env-keys ["sarah"])
(create-account "Sarah" 100.25)
(env-keys ["james"])
(create-account "James" 250.0)
(pay "Sarah" "James" 25.0)
(commit-tx) -
Execute the
payments.replfile with the following command:pact payments.repl --trace
Ensure that the REPL output aligns with expected results.
Review
You have now built and tested contract interoperability using separate user authorization and payment modules.
In this tutorial, you learned how to import functions defined in one module so they can be used in another module and tested transactions that required both modules to successfully complete tasks.
The tutorial introduced the Pact load and use keywords and demonstrated the basics of using them in your own modules.