Loans in multiple tables
The Loans and database management project is designed to demonstrate working with multiple tables and writing more complex functions to build more complete applications. For this project, you'll build a smart contract with tables for adding and manipulating loan information with secure interactions for module administrators.
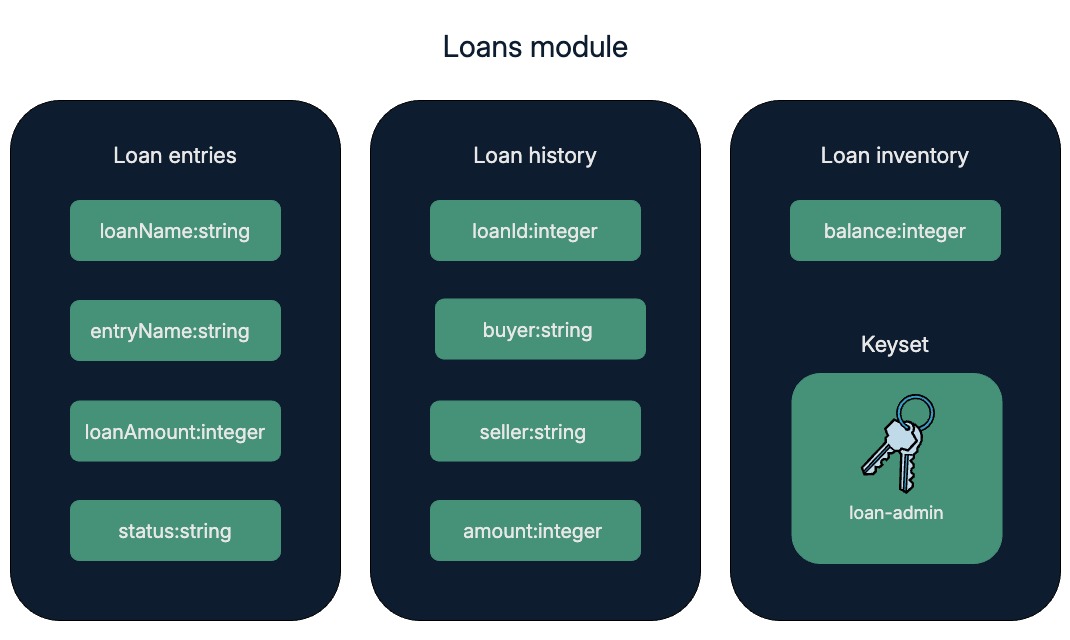
For this project, you'll create three tables in the loans module:
- A
loanstable for storing loan holder information. - A
loan-historytable for tracking loan history. - A
loan-inventorytable for holding the loan inventory balance.
Before you begin
Before starting this project, verify your environment meets the following basic requirements:
- You have a GitHub account and can run
gitcommands. - You have installed the Pact programming language and command-line interpreter.
- You have installed the
kadena-clipackage and have a working directory with initial configuration settings. - You have a local development node that you can connect to that runs the
chainweb-nodeprogram, either in a Docker container or on a physical or virtual computer. - You must have at least one account that's funded with KDA on at least one chain for deployment on the local development network or the Kadena test network.
- You should be familiar with the basics for defining modules and using keysets.
Get the starter code
To get started:
-
Open a terminal shell on your computer.
-
Clone the
pact-coding-projectsrepository by running the following command:git clone https://github.com/kadena-docs/pact-coding-projects.git -
Change to the
05-loansdirectory by running the following command:cd pact-coding-projects/05-loansIf you list the contents of this directory, you'll see the following files:
starter-loans.pactprovides a starting point with the framework for building theloansmodule.project-stepsprovides solutions and test cases for completing each part of the coding project.finished-contractsprovides the final code for theloans.pactmodule and the finalloans.repltest cases for verifying module functions.
-
Open and review the
starter-loans.pactfile.This file outlines the tasks you need to complete for the Loans project. Follow the embedded instructions to work through the coding challenges on your own or use the detailed instructions and code provided in the next sections.
Define the module and keyset
As you might have seen in other coding projects, the first step in creating a new module requires defining or identifying a namespace and an administrative owner for the module.
To start the module declaration:
-
Open the
starter-loans.pactfile in your code editor and save it asloans.pact. -
Specify the namespace and a define a keyset for the module to use.
(namespace "free")
(define-keyset "free.loans-admin" (read-keyset "loan-admin-keyset")) -
Define the
loansmodule governed by theLOAN_ADMINcapability and enforced to use thefree.loans-adminkeyset:(module loans LOAN_ADMIN
(defcap LOAN_ADMIN ()
(enforce-guard "free.loans.loans-admin"))
) -
Create a
loans.replfile in you code editor to prepare the environment for testing theloansmodule.For example, add test keys and data to define the namespace in your working environment and to load the module:
(env-keys ["loan-admin-keyset"])
(env-data { "loans-admin":
{ "keys": ["loan-admin-keyset"], "pred": "keys-all" } })
(begin-tx "Define namespace")
(define-namespace "free" (read-keyset "loans-admin" ) (read-keyset "loans-admin" ))
(commit-tx)
(begin-tx)
(load "loans.pact")
(commit-tx)
Define the schemas and tables
To define the schemas and tables:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Define the
loanschema and the table that uses theloanschema.(defschema loan
loanName:string
entityName:string
loanAmount:integer
status:string
)
(deftable loans:{loan}) -
Define the
loan-historyschema and the table that uses theloan-historyschema.(defschema loan-history
loanId:string
buyer:string
seller:string
amount:integer
)
(deftable loan-history-table:{loan-history}) -
Define the
loan-inventoryschema and the table that uses theloan-inventoryschema.(defschema loan-inventory
balance:integer
)
(deftable loan-inventory-table:{loan-inventory})
Define constants
To define the constants for loan status:
-
Define an
INITIATEDconstant that contains the status description for loans that have been initiated using the "initiated" comment.(defconst INITIATED "initiated") -
Define an
ASSIGNEDconstant that contains the status description for loans that have been assigned using the "assigned" comment.(defconst ASSIGNED "assigned")
Define functions
For this coding project, the loans module provides nine functions to provide comprehensive features for loan management.
You can define them in any order.
inventory-keytakesloanId:stringandowner:stringto create a composite key ofloanId:owner.create-a-loantakesloanId,loanName,entityName, andloanAmountto create a loan entry.assign-a-loantakestxid,loanId,buyer, andamountto assign a loan.sell-a-loantakestxid,loanId,buyer,seller, andamountto sell a loan.read-a-loantakesloanIdto read values from theloanstable for a givenloanId.read-all-loansselect all values from theloanstable withconstantlyset to true.read-inventory-pairtakeskeyto setinventory-keyandbalancefor the providedkey.read-loan-inventorymaps the value ofread-inventory-pairto the keys of theloan-inventory-table.read-loans-with-statustakesstatusto select all values from theloans-tablewherestatusequals the providedstatus.
Define the inventory-key function
To define the inventory-key function:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Start the
inventory-keyfunction definition with the keyworddefunand add the parametersloanId:stringowner:string.(defun inventory-key:string (loanId:string owner:string)
) -
Create a composite key from the
ownerandloanIdin the formatloanId:owner.(defun inventory-key:string (loanId:string owner:string)
(format "{}:{}" [loanId owner])
)
Define the create-a-loan function
To define the create-a-loan function:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Start the
create-a-loanfunction with the parametersloanId,loanName,entityName, andloanAmount. -
Insert the values for the new loan
loanIdinto theloanstable.(defun create-a-loan:string (loanId:string loanName:string entityName:string loanAmount:integer)
(insert loans loanId {
"loanName":loanName,
"entityName":entityName,
"loanAmount":loanAmount,
"status":INITIATED
})
) -
Insert the values for a new loan into the
loan-inventorytable.(defun create-a-loan:string (loanId:string loanName:string entityName:string loanAmount:integer)
(insert loans loanId {
"loanName":loanName,
"entityName":entityName,
"loanAmount":loanAmount,
"status":INITIATED
})
(insert loan-inventory-table (inventory-key:string loanId:string entityName:string){
"balance": loanAmount
})
)
Define the assign-a-loan function
To define the assign-a-loan function:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Start the
assign-a-loanfunction with the parameterstxid,loanId,buyer, andamount. -
Read from the
loanstable usingloanIdand bind variables to the column values.(defun assign-a-loan:string (txid loanId buyer amount)
(with-read loans loanId {
"entityName":= entityName,
"loanAmount":= issuerBalance
}
) -
Insert values into
loan-history-tableusing the value of thetxidparameter.(insert loan-history-table txid {
"loanId":loanId,
"buyer":buyer,
"seller":entityName,
"amount":amount}
) -
Insert values into the
loan-inventory-tablewith the parametersinventory-key,loanId, andbuyer.(insert loan-inventory-table (inventory-key loanId buyer) {
"balance":amount
}) -
Update the
loan-inventory-tablefor the row matching the parametersinventory-key,loanId, andentityNamewith the new balance of the issuer.(update loan-inventory-table (inventory-key loanId entityName){
"balance": (- issuerBalance amount)
})) -
Update the
statusin theloanstable for the specifiedloanId.(update loans-table loanId {
"status": ASSIGNED
})
If you want to test the functions that you've defined so far, you can update the loans.pact file to create the tables and the loans.repl file with transactions that call the functions.
If you aren't sure how to make these changes, continue defining the functions, then follow the steps in Test functions in the REPL.
Define the sell-a-loan function
To define the sell-a-loan function:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Start the
sell-a-loanfunction with the parameterstxid,loanId,buyer,seller, andamount. -
Read from the
loan-inventory-tabletable using the parametersinventory-key,loanId, andsellerand bindbalanceto value ofprev-seller-balance.(defun sell-a-loan:string (txid loanId buyer seller amount)
(with-read loan-inventory-table (inventory-key loanId seller)
{"balance":= prev-seller-balance} -
Read from the
loan-inventory-tableusing the parametersinventory-key,loanId, andbuyer, assign balance to 0, and bindbalanceto value ofprev-buyer-balance.(with-default-read loan-inventory-table (inventory-key loanId buyer)
{"balance" : 0}
{"balance":= prev-buyer-balance} -
Insert values into the
loan-history-tableat the giventxid.(insert loan-history-table txid {
"loanId":loanId,
"buyer":buyer,
"seller":seller,
"amount": amount
}) -
Update the
loan-inventory-tablewith the parametersinventory-key,loanId, andseller, and set thebalanceto theprevious-seller-balanceminus theamount.(update loan-inventory-table (inventory-key loanId seller)
{"balance": (- prev-seller-balance amount)}) -
Write to the
loan-inventory-tablewith the parametersinventory-key,loanId, andbuyer, set thebalanceto theprevious-buyer-balanceplus theamount.(write loan-inventory-table (inventory-key loanId buyer)
{"balance": (+ prev-buyer-balance amount)})))
)
Define the read-a-loan function
To define the read-a-loan function:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Start the
read-a-loanfunction with the parameterloanId. -
Read all of the values from the
loanstable at the givenloanId.(defun read-a-loan:object (loanId:string)
(read loans loanId))
Define the read-all-loans function
To define the read-all-loans function:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Start the
read-all-loansfunction with no parameters. -
Select all values from the
loanstable that haveconstantlyset to true.(defun read-all-loans:list ()
(select loans (constantly true)))
Define the read-inventory-pair function
To define the read-inventory-pair function:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Start the
read-inventory-pairfunction with the parameterkey. -
Set the
inventory-keyto the providedkey. -
Set the
balancevalue of the balance in theloan-inventory-tableto the value of thekey.(defun read-inventory-pair:object (key)
{"inventory-key":key,
"balance": (at 'balance (read loan-inventory-table key))}
)
Define the read-loan-inventory function
To define the read-loan-inventory function:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Start the
read-loan-inventoryfunction with no parameters. -
Map the value of the
read-inventory-pairto thekeysin theloan-inventory-table.(defun read-loan-inventory:list ()
(map (read-inventory-pair) (keys loan-inventory-table)))
Define the read-loans-with-status function
To define the read-loans-with-status function:
-
Open the
loans.pactfile in your code editor. -
Start the
read-loans-with-statusfunction that takes the parameterstatus. -
Select all values from the
loanstable where the status equals thestatusparameter.(defun read-loans-with-status:list (status)
(select loans-table (where "status" (= status)))
Complete the module declaration
Complete the loans module by closing the module declaration and create the tables.
To complete the loans module:
-
Finish the module declaration with a closing parenthesis, if you haven't already done so.
)
(create-table accounts-table) -
Create the tables defined for the module declaration, if you haven't already done so.
(create-table loans)
(create-table loan-inventory-table)
(create-table loan-history-table)
Test functions in the REPL
To test the loans module, you need to add transactions to the loans.repl file.
To test the functions in the loans.pact file:
-
Open the
loans.replfile. -
Add a transaction that loads the
loans.pactfile and then calls the functions that update the loan tables similar to the following:(begin-tx "Call functions that update loan tables")
(load "loans.pact")
(inventory-key "loanId-1" "Las Pistolas") ;; loanId, owner
(create-a-loan "loanId-1" "Ponderosa" "Valley Credit" 16000) ;; loanId, loanName, entity, amount
(assign-a-loan "txid-1" "loanId-1" "Studio Funding" 10000) ;; loanId, buyer, amount
(sell-a-loan "txid-2" "loanId-1" "buyer2" "Studio Funding" 2000) ;; loanId, seller, buyer, amount
(commit-tx)Because you're loading the module and calling the functions in the same transaction, you don't need to include the namespace and module name to call the functions.
-
Add a transaction that calls the functions that read loan information from the loan tables similar to the following:
(begin-tx "Call functions that read loan information")
(use free.loans)
(create-a-loan "loanId-2" "Renovation" "RiverBank" 140000)
(read-a-loan "loanId-1")
(read-all-loans)
(read-loan-inventory)
(read-loans-with-status INITIATED)
(read-loans-with-status ASSIGNED)
(commit-tx)In this example, you first specify that you want to use the module where the functions are defined using its namespace and module name. Similar to loading the module, you can then call individual function without including the namespace and module name.
-
Add transactions that call the individual functions similar to the following:
(begin-tx "Test inventory-key function")
(free.loans.inventory-key "loanId-3" "Pistolas")
(commit-tx)
(begin-tx "Test create-a-loan function")
(free.loans.create-a-loan "loanId-3" "Pistolas" "Capital Bank" 11000)
(commit-tx)
(begin-tx "Test assign-a-loan function")
(free.loans.assign-a-loan "txid-3" "loanId-3" "Buyer 1" 10000) ;; loanId, buyer, amount
(commit-tx)In this example, you must specify the module where the functions are defined using the namespace and module name.
-
Open a terminal shell on your computer and test execution by running the following command:
pact --trace loans.replYou should see that the transactions are successful with output similar to the following:
...
loans.pact:4:3:Trace: Loaded module free.loans, hash 6SCj9hDm0ANSVOqbmY3gwF4SXg9BaRi-7cV8-FbqJDY
loans.pact:162:0:Trace: TableCreated
loans.pact:163:0:Trace: TableCreated
loans.pact:164:0:Trace: TableCreated
loans.repl:11:2:Trace: loanId-1:Las Pistolas
loans.repl:12:2:Trace: Write succeeded
loans.repl:13:2:Trace: Write succeeded
loans.repl:14:2:Trace: Write succeeded
loans.repl:15:0:Trace: Commit Tx 1: Call functions that update loan tables
loans.repl:17:0:Trace: Begin Tx 2: Call functions that read loan information
loans.repl:18:3:Trace: Using free.loans
loans.repl:19:3:Trace: Write succeeded
loans.repl:20:3:Trace: {"entityName": "Valley Credit","loanAmount": 16000,"loanName": "Ponderosa","status": "assigned"}
loans.repl:21:3:Trace: [{"entityName": "Valley Credit","loanAmount": 16000,"loanName": "Ponderosa","status": "assigned"} {"entityName": "RiverBank","loanAmount": 140000,"loanName": "Renovation","status": "initiated"}]
loans.repl:22:3:Trace: [{"inventory-key": "loanId-1:Studio Funding","balance": 8000} {"inventory-key": "loanId-1:Valley Credit","balance": 6000} {"inventory-key": "loanId-1:buyer2","balance": 2000} {"inventory-key": "loanId-2:RiverBank","balance": 140000}]
loans.repl:23:3:Trace: [{"entityName": "RiverBank","loanAmount": 140000,"loanName": "Renovation","status": "initiated"}]
loans.repl:24:3:Trace: [{"entityName": "Valley Credit","loanAmount": 16000,"loanName": "Ponderosa","status": "assigned"}]
loans.repl:25:0:Trace: Commit Tx 2: Call functions that read loan information
loans.repl:27:0:Trace: Begin Tx 3: Test inventory-key function
loans.repl:28:2:Trace: loanId-3:Pistolas
loans.repl:29:0:Trace: Commit Tx 3: Test inventory-key function
loans.repl:31:0:Trace: Begin Tx 4: Test create-a-loan function
loans.repl:32:2:Trace: Write succeeded
loans.repl:33:0:Trace: Commit Tx 4: Test create-a-loan function
loans.repl:35:0:Trace: Begin Tx 5: Test assign-a-loan function
loans.repl:36:2:Trace: Write succeeded
loans.repl:37:0:Trace: Commit Tx 5: Test assign-a-loan function
Load successful -
Ensure that the REPL output aligns with expected results.
Review
You have now built and tested a smart contract that manipulates loan information in three tables with a robust set of functions.